
By Jessica Duffy - USEA Staff
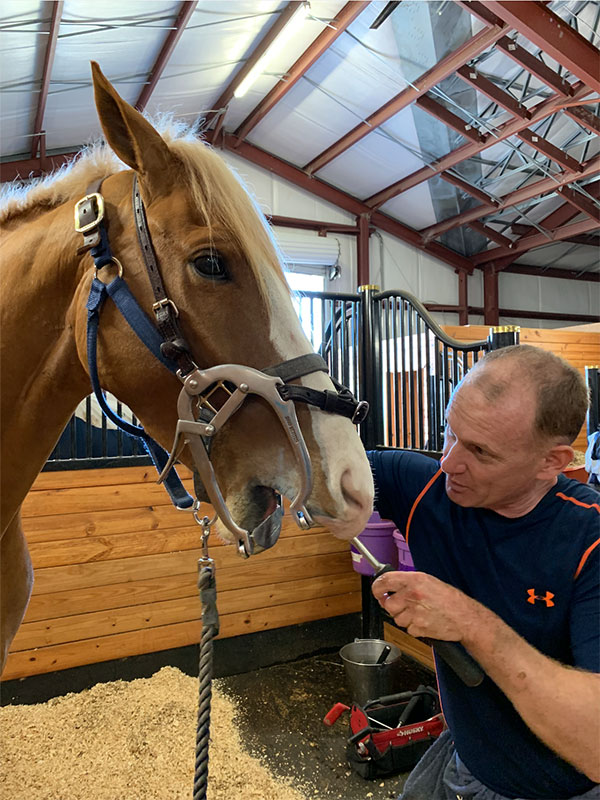
“To understand why we do dentistry and what the aims are, you need to understand about anatomy – how the teeth are set up – and how horses chew,” began Dr. James Brown, Clinical Associate Professor of Equine Surgery at Virginia Tech’s Marion duPont Scott Equine Medical Center in Leesburg, Virginia. “They chew on a side-to-side motion versus an up-and-down motion, the way we chew. So, it’s important that they have that range of motion.”
Horses spend an average of 10 hours a day eating and erupt anywhere from 2-6 millimeters of tooth per year, so making sure that your horse’s teeth are taken care of is crucial to their overall health and wellbeing. Furthermore, issues with a horse’s teeth can translate into issues while they are under saddle, as the bit and bridle can become uncomfortable if the horse’s teeth aren’t properly cared for.
“It basically boils down to two things,” Brown said. “First, we’re thinking about oral comfort. When you have sharp points, they can cause trauma to the surrounding soft tissue. They usually occur on the outer side of the upper cheek teeth and the lingual side – the tongue side – of the lower cheek teeth. Second, we want to prevent malocclusions. What’s a malocclusion? It’s a malalignment of how the cheek teeth or incisors should be arranged so that it interferes with that lateral excursion – that side-to-side motion – of the mandible.”
Brown described horses’ teeth, which erupt continually, as a natural grinding stone. The side-to-side motion wears teeth down, but they don’t always wear evenly. That’s where equine dentistry comes in – to maintain balance that is created by uneven wear patterns.
When things don’t line up properly, the wear patterns can be even more dramatic, causing malocclusions. “When all the upper maxillary cheek teeth arcades aren’t in alignment with all the lower mandibular cheek teeth, it can lead to part of a tooth not having an opposing tooth to grind against, and therefore the tooth will keep erupting and develop overgrowths.” An example of this is what is known as “parrot mouth.”
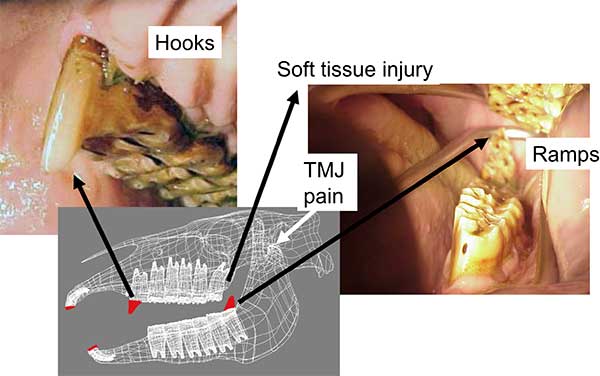
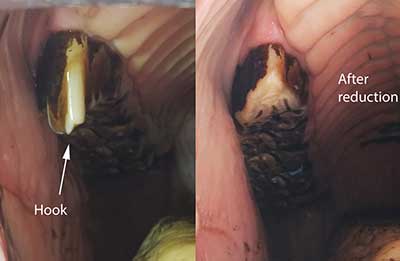
Parrot mouth occurs when the mandible is sitting back behind and the maxillary incisors extend out over the mandibular incisors. “The horse develops a ramp and a hook, and usually the incisors don’t line up either, so you’ll get an overgrowth of one or both. You might say, ‘Well, what’s the problem with that?’ Eventually, the ramps will dig into the soft tissue. The problem with this kind of anatomy, this malocclusion, is that it prevents the normal rostral caudal movement of the mandible – sliding forward and back – with the flexion of the head. When you have a hook and a ramp and uneven incisors, that locks the jaw and usually transfers to temporomandibular pain.” Riders will notice that the horse resists the bit, especially when asked to flex at the poll.
Wave mouth is another commonly seen malocclusion where malalignment of the upper and lower teeth can cause the teeth to shift. “If a horse doesn’t have good alignment of the cheek teeth, it puts preferential pressure on certain teeth that then go on and start shifting,” Brown continued. “A tooth can rock forward and that opens up a gap, and then food can pack into the gap, resulting in periodontal disease.”
When the equine dentist finds sharp points or abnormal wear on the teeth, this can be corrected by floating. “Floating is a masonry term,” Brown explained, “but we use it in dentistry to say removing sharp points – it’s the technique of smoothing over the sharp edges. We want all the teeth to wear at the same level and the same rate and so we’re trying to maintain good occlusal surfaces for grinding. We don’t want to be too aggressive – we want to maintain function as we correct the problem.”
Having a horse’s teeth examined regularly is crucial to their oral health, and consequently their overall health. Brown asserted that it’s important to have your horse’s teeth examined regularly to keep issues from developing. “For young horses, every 6 to 8 months. With middle-aged horses, you can probably get away with 12 months, although performance horses really need it every 6 to 8 months if they’ve got a bit in their mouth all the time. The cost of prevention going to save you a lot of trouble in the long run.”
About Dr. James Brown, BVSc, MS, Diplomate ACT, Diplomate ACVS
Dr. Brown received his Bachelor of Veterinary Science with honors from the University of Melbourne in Melbourne, Australia, and also earned a graduate diploma in agricultural economics from the University of New England in Armidale, New South Wales, Australia. After conducting research on upper airway diseases in racehorses, he completed a residency in equine reproduction at the University of California at Davis and subsequently achieved board certification in the American College of Theriogenologists. This certification acknowledges exceptional expertise in animal reproduction and obstetrics.
Dr. Brown earned his master’s degree in biomedical and veterinary sciences by completing a three-year surgical residency at the Equine Medical Center, which included conducting research on methods for culturing stem cells. He achieved Diplomate status through the American College of Veterinary Surgeons in 2011.
This article originally appeared on US Eventing and is published here with permission.
Find more informative articles in our section on Health & Education.

































